반응형
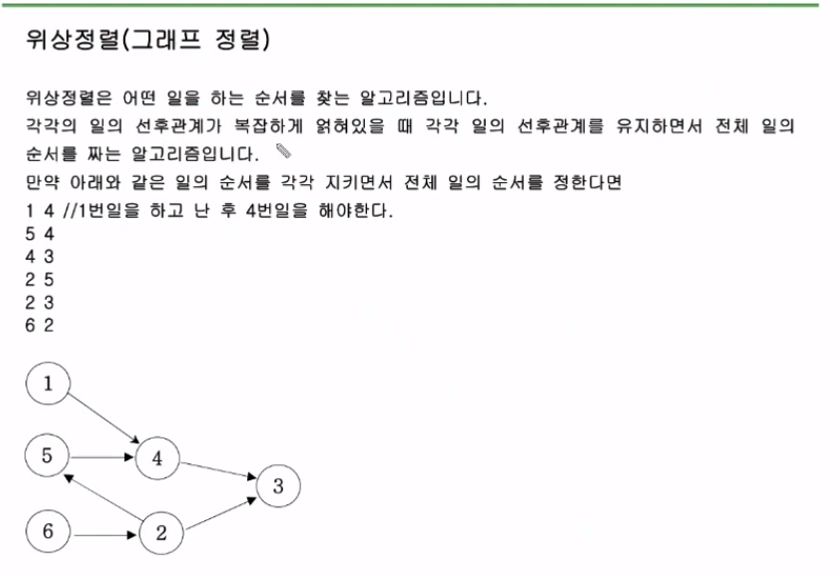

위상정렬
- 일의 선후관계를 유지하면서 그래프를 짜는 알고리즘
- Degree (진입차수배열)을 만든다.
- 진입차수의 배열 값은 선행되는 작업의 갯수
- 진입차수배열 값이 0이면 선행되는 작업이 없다는 뜻
- Queue를 만들어서 진입차수가 0인 노드를 넣는다.(선행되는작업이없는노드)
dgree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1,6실행 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 2,5실행 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4,3실행 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
즉, 일을 순서대로 지키면서 BFS를 돌리는 알고리즘이다.
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
6 6
1 4
5 4
4 3
2 5
2 3
6 2
*/
int n, m, a, b, score;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>>graph(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
vector<int> degree(n + 1);
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> a >> b;
graph[a][b] = 1;
degree[b]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (degree[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
}
while (!q.empty())
{
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << now << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (graph[now][i] == 1)
{
degree[i]--;
if (degree[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
반응형
'Algorithm > Algorithm_Lecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [강의]80. 다익스트라 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.04 |
|---|