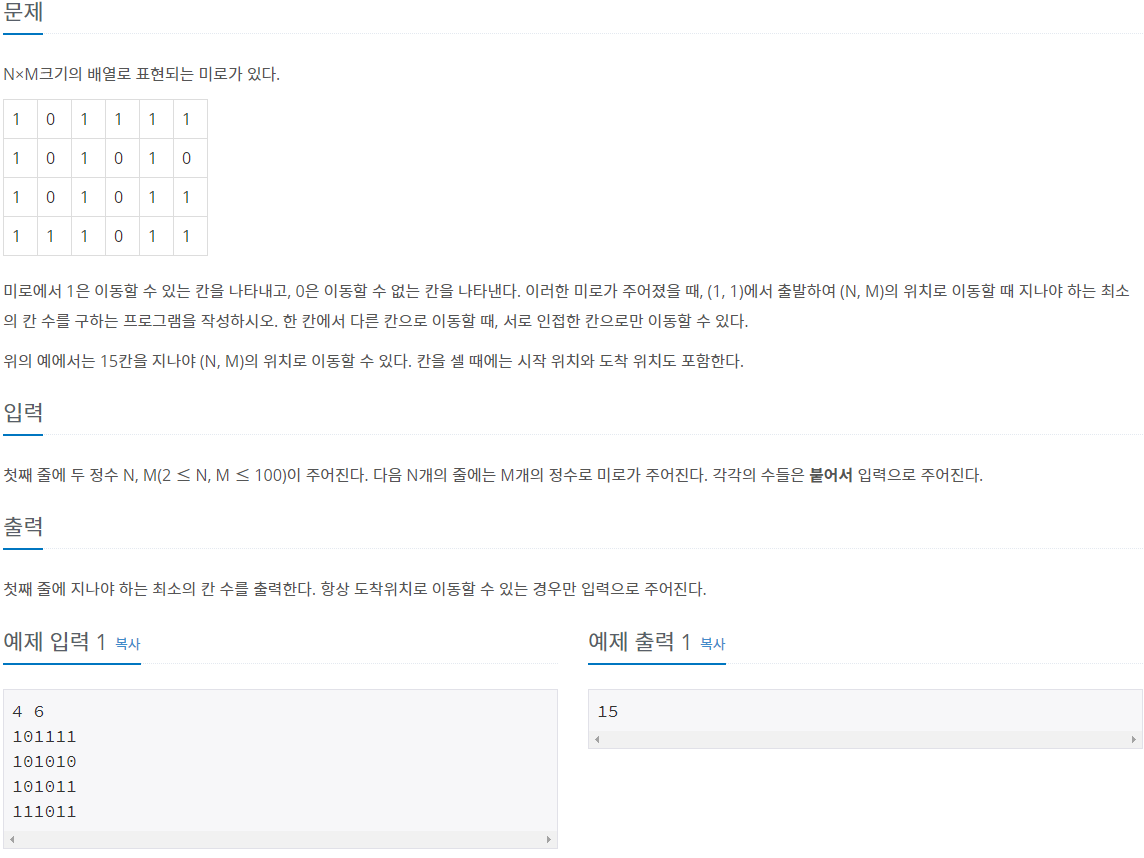
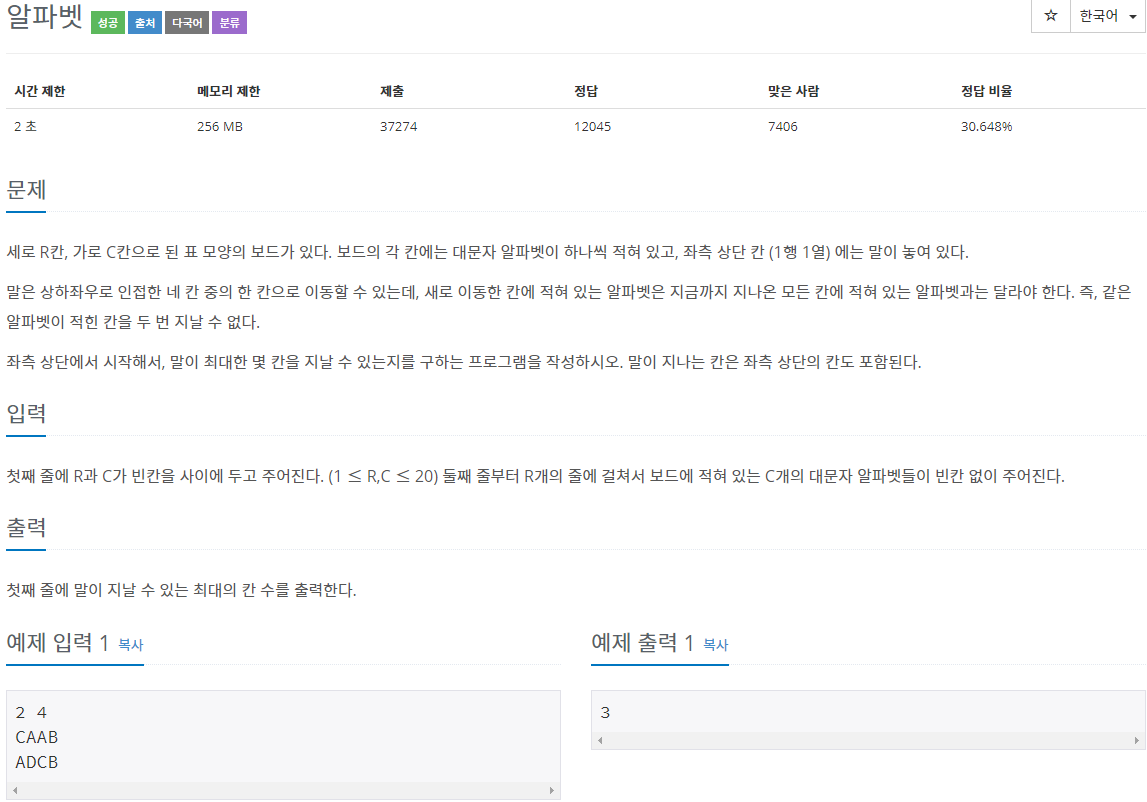
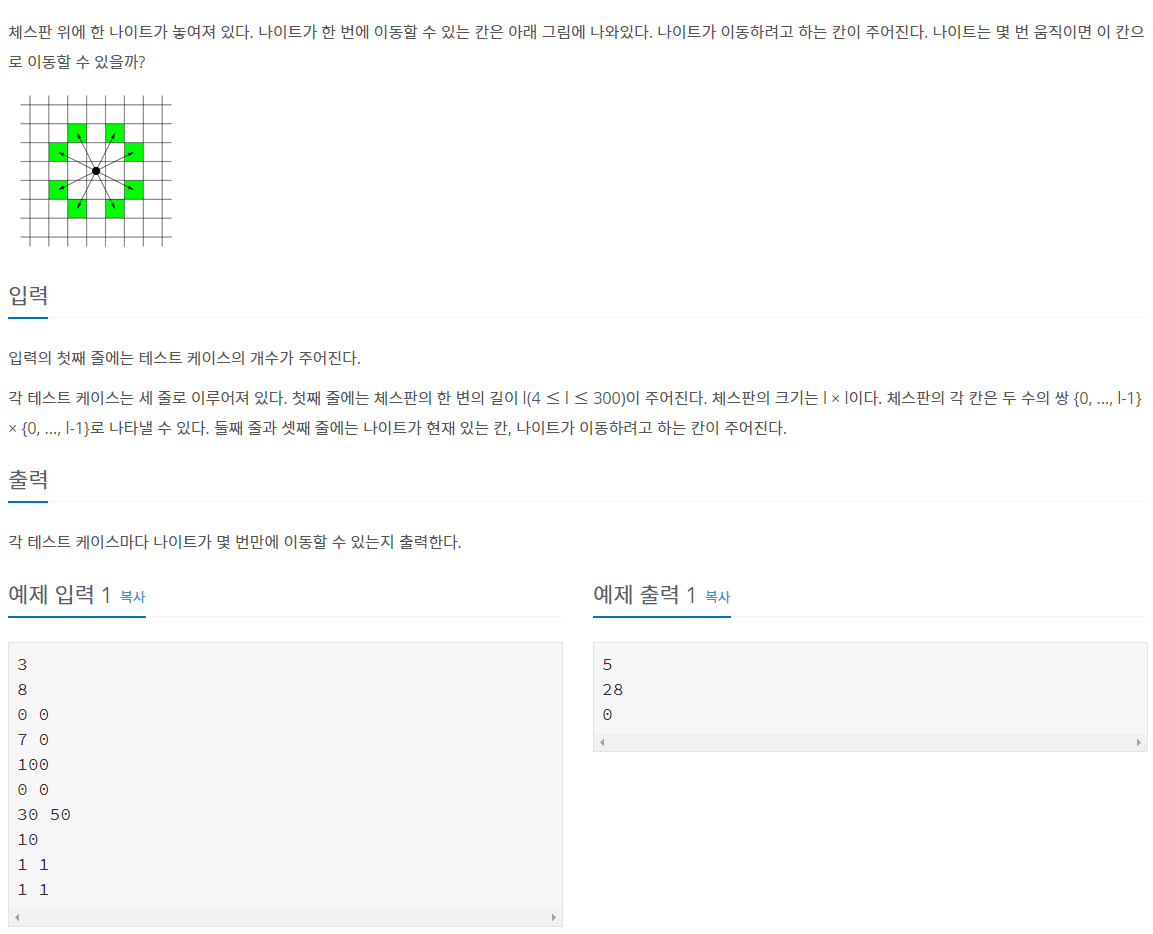
7562번: 나이트의 이동
체스판 위에 한 나이트가 놓여져 있다. 나이트가 한 번에 이동할 수 있는 칸은 아래 그림에 나와있다. 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어진다. 나이트는 몇 번 움직이면 이 칸으로 이동할 수 ��
www.acmicpc.net
문제풀이
- 이동 dx, dy를 잘 체크해준다.
- 이동 할 때마다 체크 및 +1 씩 해준다.
- 도착 지점이면 바로 break;로 나온다.
c++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
/*
8
0 0
7 0 */
using namespace std;
int k, sa, sb, ea, eb;
int visit[1000][1000];
const int dx[] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
const int dy[] = { 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1 };
int ans;
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
int num;
};
queue <Point> q;
vector<int> answer;
void input()
{
cin >> k;
cin >> sa >> sb;
cin >> ea >> eb;
}
int solve()
{
visit[sa][sb] = 1;
q.push({ sa, sb, 0 });
while (!q.empty())
{
Point pp = q.front();
int x = pp.x;
int y = pp.y;
int nn = pp.num;
q.pop();
for (int w = 0; w< 8; w++)
{
int nx = x + dx[w];
int ny = y + dy[w];
int nnn = nn + 1;
if (nx == ea && ny == eb)
{
return nnn;
}
if (nx >= k || ny >= k || nx < 0 || ny < 0)
{
continue;
}
if (visit[nx][ny] == 1)
continue;
if (visit[nx][ny] == 0)
{
visit[nx][ny] = 1;
q.push({ nx, ny, nnn });
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void Init()
{
queue <Point> q;
memset(visit, 0, sizeof(visit));
ans = 0;
}
int main()
{
int t; cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++)
{
input();
Init();
int anss = solve();
cout << anss << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Java
package Z_J_Code;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Location12 {
int x;
int y;
int level;
public Location12 (int x, int y, int level) {
this.x= x;
this.y=y;
this.level= level;
}
}
public class Main3 {
static int L;//체스판 크기
//static int board[][];
static int visited[][];
//static Stack<Location> stk= new Stack<Location>();
static Queue<Location12> que = new LinkedList<Location12>();
static int dir_x [] = {-1, -2,-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
static int dir_y []= {-2, -1,1, 2, 2, 1,-1, -2};
static int count=0;
static int search (int x, int y, int endX, int endY) {
//stk.push(new Location(x,y));
que.add(new Location12(x,y,0));
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
Location12 current =que.poll();
//if (current.x==endX && current.y==endY) return;
//count++;
//System.out.println("curent:"+ current.x+ ","+ current.y+ ","+ current.level);
for (int i=0; i<dir_x.length; i++) {
int nextX= current.x+dir_x[i];
int nextY= current.y+dir_y[i];
int level= current.level+1;
if (nextX==endX && nextY==endY) {
//System.out.println(nextX+", "+ nextY);
return level;
}
if (nextX>=0 && nextX<L && nextY>=0 && nextY<L && visited[nextX][nextY]==0) {
//System.out.println(nextX+", "+ nextY+ ","+ level);
visited[nextX][nextY]=1;
que.add(new Location12 (nextX, nextY,level));
//count++;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc =Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); //테케 갯수
for (int i=0; i<tc; i++) {
que.clear();
count=0;
L= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); //체스판 크기
//board = new int [L][L];
visited = new int [L][L];
for (int row[]: visited) {
Arrays.fill(row, 0);
} //초기화시킴
String input= br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st= new StringTokenizer(input);
int startX= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int startY= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
input = br.readLine();
st= new StringTokenizer(input);
int endX= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int endY= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (startX==endX && startY==endY) System.out.println(0);
else {
visited[startX][startY]=1;
System.out.println(search(startX, startY, endX, endY));
}
//System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 1654] 랜선 자르기_이분탐색 (0) | 2020.09.07 |
|---|---|
| [백준 9012] 괄호 (Java) (0) | 2020.09.07 |
| [백준 2664] 촌수계산 (C++, Java) (0) | 2020.09.06 |
| [백준 2309] 일곱 난쟁이 (C++, Java) (0) | 2020.09.06 |
| [백준 2178] 미로찾기 (C++, Java) (0) | 2020.09.06 |